StarQuest Technical Documents
SQL Server Authentication Considerations
Last Update: 30 July 2018
Product: StarQuest Data Replicator
Version: 3.76
Article ID: SQV00DR022
Abstract
The StarQuest Data Replicator service (SQDRSVC) interacts with SQL Server security for these purposes:
- To read from or write to the SQDR control tables when using SQL Server (rather than DB2 LUW) for a control database
- To read from a SQL Server object that is a replication source
- To write to a SQL Server object that is a replication destination
The SQDR Plus services (sqdr+jetty and sqdr+capagent) interact with SQL Server when SQL Server is being used as an incremental replication. In this case, the account needs read access and sufficient authority to create tables and stored procedures in a new schema (e.g. SQDR) on the host database. It also needs authority to alter the database and all subscribed tables to use CHANGE TRACKING; this may require administrative privileges. If SQDR Plus is using Change Data Capture rather than Change Tracking, different privileges may be needed. See SQDR Plus SQL Server User Authorities for details.
In each of these situations, the service must log in to SQL Server using a valid login and password. The security properties of the SQL Server and of the ODBC Data Source or connection string dictate which login and password should be used to connect to the SQL Server and how SQDR determines default settings.
This document outlines the SQDR configuration and usage considerations when using a particular SQL Server authentication mode. While these instructions address many of the configuration steps involved with setting up a new SQDR installation, this document is intended to supplement, but not replace, the SQDR or SQDR Plus Quick Start Guides.
- Background
- Configuring the SQL Server ODBC DSN
- Configuring the SQDR Service
- Defining a SQDR Source or Destination
- Creating a Replication Subscription
- SQL Server Authentication
- Windows Authentication
- Additional Security Considerations
Background
SQL Server can operate in one of two security modes: Windows Authentication mode or SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode (mixed mode). For both authentication modes, a Windows login can be used to connect to the SQL Server. Only in the latter case will SQL Server credentials be accepted. To determine the security mode in effect, open the SQL Server Management Studio, right-click on the server in the left pane and select Properties. Select Security on the left and note the authentication mode. Refer to your SQL Server documentation for more information about managing security levels and authentication modes.
Solution
The type of authentication to be used to access SQL Server (by the SQDR service) should be decided on during the planning stages of a SQDR implementation. To simplify the implementation, we generally recommend the use of SQL Server authentication. However, SQDR fully supports Windows authentication as well.
The type of authentication will affect the following SQDR configuration operations:
Configuring the SQL Server ODBC DSN
SQDR uses the SQL Server ODBC DSN configuration to determine which type of user credentials to expect when connecting to the SQL Server. Note that the login, whether SQL Server or Windows, must have appropriate permissions for the operations the SQDR Service will perform, such as read/write access to the destination database.
Configuring the SQDR Service
On the first panel of the SQDR Configuration wizard, you will be prompted to select the ODBC DSN or supply the connection string that the SQDR Service should use to connect to the SQL Server that contains the SQDR control tables and to provide the user credentials for the connection. The user and password fields are displayed only If the SQL Server ODBC DSN is configured for SQL Server authentication.
Defining a SQDR Source or Destination
When defining a SQDR Source or Destination for the SQL Server, select the SQL Server ODBC DSN, or (if using connection strings), the SQL Server Native Client 11 ODBC driver or ODBC Driver 13 for SQL Server. In addition, choose the Authentication Method (Remote Credentials or Use Integrated Security). The user and password fields are displayed only when the Remote Credentials button is selected.
Creating a Replication Subscription
In the Destination panel of the SQDR subscription wizard, SQDR automatically provides the default Object Schema based on the login used in the Destination properties. When using Windows authentication, the default value provided by SQDR for the Object Schema is not typically valid and must be manually modified.
Note: It is not necessary to use the same type of login for the Source or Destination as the one used during the SQDR Configuration. For example, if you would like the SQDR service to use a Windows login to connect to its control database, but would prefer that the SQDR Source/Destination use a SQL Server login, you only need to create a separate SQL Server ODBC DSN configured to accept a SQL Server login and use it when creating the Source/Destination in SQDR. You can also use DSN-less connection strings for Source, Destination, or control database.
To help you decide which authentication type to use, review the information below for each authentication type. Or, if you aready know which authentication type is best suited for your environment, choose the appropriate link below to be directed to the specific SQDR configuration steps.
SQL Server Authentication
Configuring the SQL Server ODBC DSN
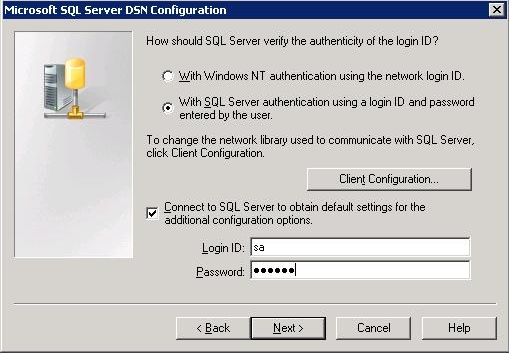
If your SQL Server is configured to use the "SQL Server and Windows Authentication" mode, you have the option of using a SQL Server user account to connect to the SQL Server. Select the option With SQL Server authentication using a login ID and password entered by the user in the DSN configuration, as shown in the image below.
Configuring the SQDR Service
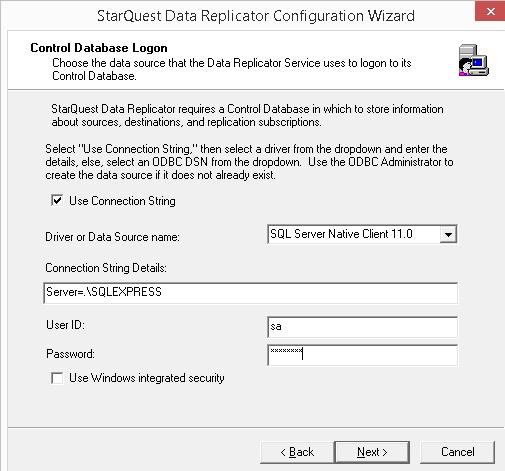
Select the SQL Server ODBC DSN from the Data Source drop down list, or select the SQL Server Native Client 11.0 or ODBC 13 for SQL Server driver and enter a SQL Server connection string, and supply a SQL Server User ID and Password, as shown in the image below.
Important note: the SQL Server login should be a member of the SQL Server sysadmin server role.
Defining a SQDR Source or Destination
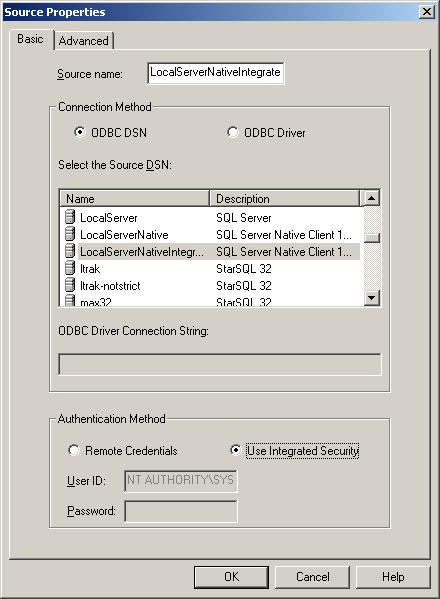
When defining a SQDR Source or Destination for the SQL Server, select the SQL Server ODBC DSN and the SQL Server login to use. The image below shows the Source Properties, but the same applies to the Destination configuration.
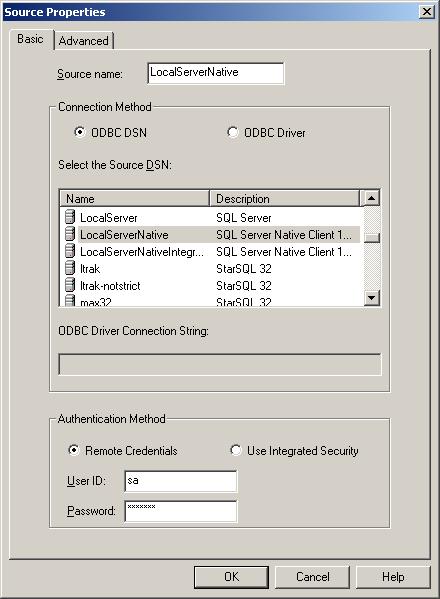
Creating a Replication Subscription
If your SQDR Destination uses a SQL Server login, SQDR will automatically populate the Object Schema field with the default schema for that login, such as "dbo". In almost all cases, no change is required. You only need to modify the Object Schema if you want to use a different schema for the destination object.
Windows Authentication
Configuring the SQL Server ODBC DSN
If you plan to use a Windows user account to connect to the SQL Server, select the With Integrated Windows Authentication in the DSN configuration, as shown in the image below.
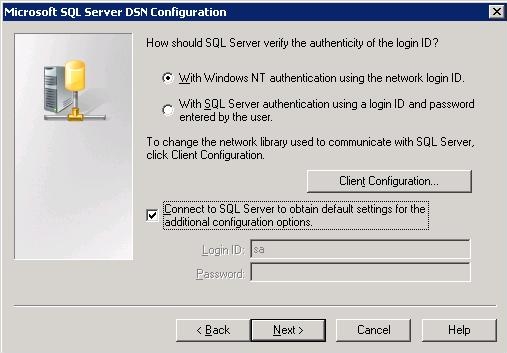
Configuring the SQDR Service
Select the SQL Server ODBC DSN from the Data Source drop down list or select the SQL Server Native Client 11.0 or ODBC 13 for SQL Server driver and enter a SQL Server connection string and select the Use Windows integrated security checkbox.
Important note: the Windows login should be a member of the SQL Server sysadmin server role.
Defining a SQDR Source or Destination with a DSN
When defining a SQDR Source or Destination for the SQL Server, select the SQL Server ODBC DSN and select the Use Integrated Security radio button. The image below shows the Source Properties, but the same applies to the Destination configuration.
Defining a SQDR Source or Destination with a DSN-less Connection String
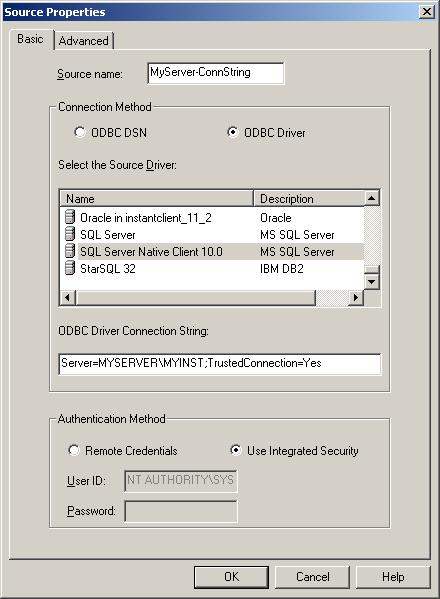
When defining a DSN-less connection string for the SQDR Source or Destination for the SQL Server, select the SQL Server driver, select the Use Integrated Security radio button, and include TrustedConnection=Yes in the connection string. The image below shows the Source Properties, but the same applies to the Destination configuration.
Creating a Replication Subscription
If the SQDR Destination is configured to use a Windows login, when creating a subscription SQDR will automatically populate the Object Schema field with the Windows login. In most cases, this is not a valid schema on the destination database. Modify the Object Schema to use a valid schema on the destination database server, such as "dbo", as shown below.
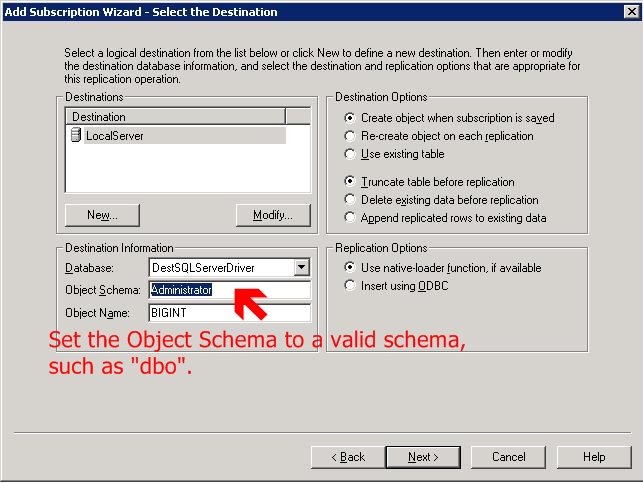
Additional Security Considerations
If the SQL Server ODBC data source being used for access to the control database is configured for Integrated Security, the SQDR service may fail to start with the following error (displayed in the Event Log):
ODBC message: SQLSTATE 08004, native error 916, [Microsoft][SQL Server Native Client 11.0][SQL Server]The server principal "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM" is not able to access the database "ControlDB4" under the current security context.
This error occurs because the service is running as a user (Local System Account) that lacks sufficient authority to the SQL Server database. The service user requires at least read/write access to tables in the database; in addition it needs the authority to create new tables if the SQL Server database is being used as an SQDR destination.
To grant these authorities on an existing database:
- Open the SQL Server Management Studio.
- Open Security/Logins in the left pane.
- For a local SQL Server instance: If NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM is not already listed under Logins, add it by right-clicking on Users and selecting New User...
Then click on the ... box next to "Login name". In the Select Login dialog, select Browse... and select NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM.
For a remote SQL Server instance: Add the machine account e.g. MyDomain\MySQDRMachine$, where MyDomain is the domain and MySQDRMachine is the name of the system running SQDR. Select that account.
You can also add the machine account with the statement
CREATE LOGIN [MyDomain\MySQDRMachine$] FROM WINDOWS
- Right click and select properties
- Choose User Mappings
- Select the checkbox next to the database (e.g. ControlDB)
- In the lower part of the dialog, there are checkboxes for Database Role Membership; Public is selected by default. For read/write access to the database, select db_datareader & db_datawriter. When using SQL Server as the SQDR control database, this is adequate to start the service, create & run snapshot sub & group, and create schedules.
- For authority to create new tables, also select db_ddladmin; this is necessary to use the SQL Server database as an SQDR destination.
When using the Data Replication Configuration application to create or update the control database, the user (either the SQL Server login entered when using Mixed Mode Authentication, or the Windows login when using Windows authentication) should be a member of the sysadmin fixed server role.
DISCLAIMER
The information in technical documents comes without any warranty or applicability for a specific purpose. The author(s) or distributor(s) will not accept responsibility for any damage incurred directly or indirectly through use of the information contained in these documents. The instructions may need to be modified to be appropriate for the hardware and software that has been installed and configured within a particular organization. The information in technical documents should be considered only as an example and may include information from various sources, including IBM, Microsoft, and other organizations.